Understanding Structural Steel Construction
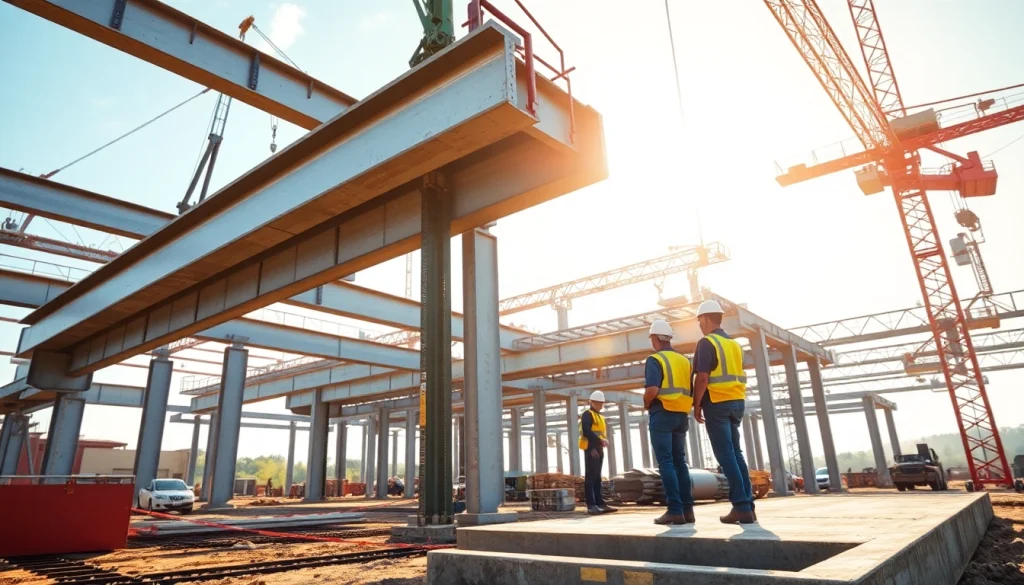
Structural steel construction plays a pivotal role in modern building practices, providing flexibility and strength to various construction projects. From skyscrapers to bridges, structural steel is a fundamental element that supports the weight and shapes the aesthetics of buildings. Its widespread use stems from its unique properties and advantages, contributing to the sustainability and longevity of structures. This article delves into various facets of structural steel construction, including its characteristics, benefits, techniques employed, and challenges faced in the industry.
What is Structural Steel?
Structural steel is a category of steel used for manufacturing construction materials in a variety of shapes. Typically composed of carbon steel with a low carbon content ranging from 0.05% to 0.25%, it is available in numerous configurations including beams, columns, and plates. To qualify as structural steel in the United States, the steel must adhere to specific standards set by ASTM International, ensuring its strength and reliability in construction applications.
Properties of Structural Steel
Structural steel exhibits several crucial properties that make it an ideal choice for construction:
- High Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Structural steel is incredibly strong, which allows for the construction of substantial structures without excess weight.
- Ductility: This property enables steel to absorb energy and deform without breaking, making it suitable for buildings that may experience earthquakes or high winds.
- Versatility: Structural steel can be fabricated into various shapes, allowing architects and engineers to design innovative structures.
- Durability: Structural steel resists the elements and can withstand harsh environments when adequately protected against corrosion.
- Recyclability: Steel can be recycled without losing its properties, making it an environmentally responsible choice for construction.
Common Applications of Structural Steel
Structural steel finds applications across various sectors, enhancing functionality and aesthetics in construction projects. Common uses include:
- Commercial Buildings: Used for frames and supporting beams, contributing to large open spaces and architectural designs.
- Bridges: Steel’s strength and resilience make it suitable for both road and rail bridges, allowing for large spans.
- Industrial Facilities: Factories and warehouses benefit from structural steel frames for durability and operational efficiency.
- Residential Structures: Increasingly popular in modern homes for its design and versatility, allowing for contemporary aesthetics and open floor plans.
Benefits of Using Structural Steel in Construction
Durability and Longevity
Structural steel is celebrated for its long lifespan, frequently surpassing 50 years in major projects when properly maintained. Its inherent properties, such as resistance to pests and rot, contribute to lower maintenance costs compared to other materials. With the right protective coatings and design considerations, structural steel can endure harsh environmental conditions, reducing the need for replacements or extensive repairs.
Cost-Effectiveness Over Time
While initial material costs for structural steel may be higher than other materials, its overall cost-effectiveness emerges through its durability and reduced maintenance needs. The faster and simpler assembly of steel structures can also translate to shorter project timelines and lower labor costs. Additionally, the ability to prefabricate components leads to less waste and increased efficiency in on-site construction.
Environmental Sustainability
As concerns for sustainability grow in the construction industry, structural steel offers eco-friendly advantages. Its recyclability means that end-of-life structures can be repurposed, significantly reducing landfill waste. Moreover, the energy efficiency associated with steel production is improving as the industry adopts greener practices, minimizing environmental impact while maintaining structural integrity.
Key Techniques in Structural Steel Construction
Welding and Fabrication Methods
Welding is a critical process in structural steel construction, enabling the creation of robust connections between different steel elements. Common welding methods include:
- Arc Welding: Utilizes an electrical arc to melt and join metal pieces.
- MIG Welding: Stands for Metal Inert Gas welding, popular for its speed and efficiency in joining steel.
- TIG Welding: Uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode for precision welding, ideal for thinner sections.
Each of these methods has its advantages depending on the project’s requirements and the steel being used.
Assembly and Erection Processes
The assembly of structural steel involves careful planning to ensure safety and efficiency. Skilled laborers often use cranes and other machinery to lift heavy steel components into place. Techniques include:
- Bolting: Often used for quick assembly, where pre-fabricated sections are bolted together.
- Welding on Site: Occasionally necessary for adjustments, fulfilling high load requirements or ensuring stability.
Site safety is paramount during these processes, requiring adherence to strict regulations and guidelines.
Quality Assurance Standards
Quality assurance is crucial in structural steel construction to ensure the integrity and safety of the completed structure. Standards such as those set forth by the American Institute of Steel Construction (AISC) guide fabrication and erection processes. Regular inspections, testing of materials, and certifications are essential steps in maintaining these quality standards.
Challenges in Structural Steel Construction
Addressing Cost Fluctuations
The cost of structural steel can fluctuate due to various factors, including raw material prices and supply chain issues. To mitigate risks, stakeholders often rely on contract terms that allow for fixed pricing or adjust pricing structures to reflect current market conditions. Effective project management and budgeting strategies can help navigate these fluctuations.
Compliance with Regulations
Structural steel construction must adhere to numerous building codes and safety regulations, which can vary by location. Ensuring compliance through detailed planning and consultation with relevant authorities is essential. Keeping up-to-date with changing regulations can be a challenge but is vital for project approval and safety.
Mitigating Safety Risks
Safety in structural steel construction is a significant concern due to the heavy materials and complex processes involved. Implementing comprehensive safety training, providing proper protective gear, and integrating safety protocols into daily operations can greatly reduce risks. Regular safety audits and updates to equipment and practices further enhance site safety.
FAQs about Structural Steel Construction
How is structural steel manufactured?
Structural steel is manufactured through a series of processes including melting, casting, and rolling to create the desired shapes and sizes for construction. This involves strict adherence to ASTM standards to ensure quality.
Can structural steel be recycled?
Yes, structural steel is highly recyclable. Its materials retain strength through reprocessing, reducing waste and resource consumption in new construction projects.
What are the safety measures in steel construction?
Key safety measures include ensuring compliance with safety regulations, providing effective training, using personal protective equipment, and regularly conducting site audits to identify potential hazards.
How does weather affect structural steel construction?
Extreme weather can delay construction timelines and affect worker safety. Proper planning, including weather assessments, scheduling, and protective measures, is essential to mitigate these impacts.
What tools are essential for structural steel construction?
Essential tools include welding machines, cranes, bolt tensioners, measuring instruments, and safety gear. Each plays a pivotal role in ensuring precision and safety during the construction process.